Google Losing Market Share: A 2024 Overview
Google, once the unchallenged titan of the search engine market, is experiencing a notable decline in its market share. This article explores the reasons behind this shift, backed by recent statistics, and examines the implications for the tech giant and the broader digital ecosystem.
Key Factors Contributing to Google’s Decline
Rise of Competitors
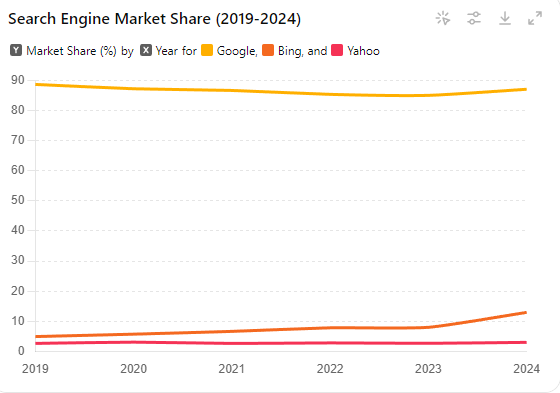
- Microsoft’s Bing: Bing, bolstered by its integration with OpenAI’s ChatGPT, has attracted users seeking enhanced AI-driven search experiences. Bing’s advanced natural language processing capabilities provide more accurate and contextually relevant results, drawing users away from Google. Bing has seen its U.S. market share grow to 13% in 2024, while its global share increased to 5.8% (Search Engine Journal) (Know Your Mobile).
- Privacy-Focused Engines: Search engines like DuckDuckGo and Brave are gaining traction among users prioritizing privacy. DuckDuckGo’s market share, though small, is steadily growing, and its usage is up by 0.51% globally in 2024 (StatCounter Global Stats).
Changing User Preferences
- Shift to Social Media and Apps: Increasingly, users are bypassing traditional search engines in favor of social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and Twitter for information and recommendations. Specialized apps for travel, shopping, and local services also reduce the need for general search engines.
- Voice Search: The rise of voice-activated assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri, and Microsoft’s Cortana has changed search habits. Users find voice search more convenient for quick queries, and these assistants do not always default to Google.
Regulatory Challenges
- Antitrust Scrutiny: Google faces heightened regulatory scrutiny and antitrust actions in multiple countries, including the European Union and the United States. These legal challenges limit Google’s ability to expand and innovate freely, impacting its market operations and strategic decisions.
- Data Privacy Laws: Stricter data privacy regulations, such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), have hindered Google’s data-driven advertising model. These laws restrict how Google collects and uses personal data, affecting its advertising revenue and market position.
Advertising Market Shifts
- Diversification of Ad Spend: Advertisers are diversifying their spending across multiple platforms, including social media giants like Facebook and Instagram, reducing their reliance on Google Ads. This shift is driven by the effectiveness of targeted advertising on social media, where user engagement tends to be higher.
- Emerging Platforms: New advertising platforms are emerging, offering innovative and cost-effective solutions. This competition is fragmenting the digital advertising market, making it harder for Google to maintain its dominance.
Statistics Highlighting the Shift
- Google’s global search engine market share dropped to 86.99% in 2024, the lowest point since tracking began in 2009. This represents a significant decline from the previous year’s 90.22% (Statista) (Search Engine Journal).
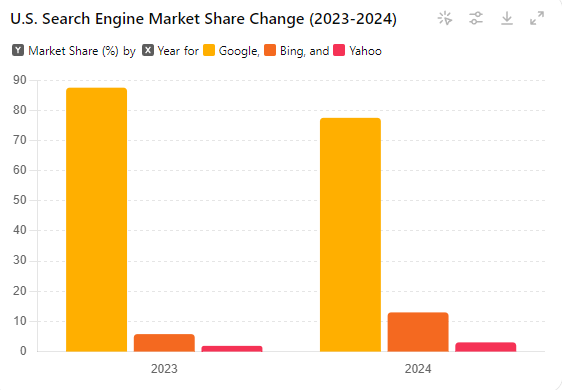
- In the United States, Google’s share of searches across all devices fell by nearly 10%, reaching 77.52%. Concurrently, Bing increased its U.S. market share to 13%, and Yahoo’s share tripled to 3.06% (Search Engine Journal) (Know Your Mobile).
- Google’s decline in market share is partly due to the increasing prevalence of “zero-click” searches, where users find the information they need directly on the search results page without clicking through to a website. On desktop, 25.6% of searches result in zero clicks, while on mobile, this figure is 17.3% (Semrush).
Implications for the Market
- Increased Competition: The entry of more players into the search engine market can lead to improved services and innovations that benefit users. Competitors are likely to focus on niche markets and specific user needs, driving overall advancements in search technology.
- Privacy-Centric Trends: A shift towards privacy-focused solutions may drive the development of new features prioritizing user data protection. This trend could reshape how search engines and digital platforms operate, emphasizing transparency and user consent.
- Regulatory Landscape: Ongoing legal challenges could reshape the digital advertising ecosystem, potentially leveling the playing field for smaller competitors. Regulations might enforce fairer competition and limit the monopolistic practices of major tech companies.
While Google remains a dominant player, the evolving digital landscape presents significant challenges to its market supremacy. Adapting to these changes will be crucial for Google to maintain its position and continue to innovate in an increasingly competitive environment. The rise of new competitors, changing user behaviors, regulatory pressures, and shifts in advertising trends collectively signal a transformative period for the search engine giant.
For further detailed insights and up-to-date statistics, industry reports and market analyses can provide a comprehensive understanding of this ongoing shift.